Exploring the World of Fair Trade Coffee: What You Need to Know
 |
| Exploring the World of Fair Trade Coffee: What You Need to Know |
What Is Fair Trade?

Fair Trade is a movement that promotes fair pay and ethical treatment for producer groups in developing countries when they export their goods to the developed world. It is regulated by a set of standards set in place by non-profit, third-party fair trade associations that award certifications to companies that adhere to the 10 principles of fair trade.
Obstacles in Developing Countries
- Few Jobs - In areas where employment opportunities are scarce, people are left with no other option than to work long hours for low wages, often in unsafe conditions.
- Low Value - If local markets become saturated, the value of locally-produced commodities (such as coffee) drops substantially.
- Unfair Trade Deals - Additionally, middlemen, or commodities traders, pay farmers lower prices than their goods are worth to raise their profits. As a result, farmers, their families, and their communities suffer.
Solutions Fair Trade Offers
- Long-Term Commitments - A true fair trade company will commit to working with the same producer for a minimum of 3 years. Real change takes time, so long-term agreements give farmers a chance to improve their methods under the guidance of their distributors. Producers who sell their goods to a fair trade company are paid livable wages for their work, are educated about human rights, and are ensured safe working conditions.
- New Markets - By selling their goods to North America and Europe, producers can get a better price because the demand is higher in those markets than at the local level.
- Eliminate Middlemen - Distributors work directly with producers. In the context of coffee, this means that green coffee buyers (who purchase coffee berries before they are roasted) travel to the developing world and meet with farmers to form trading relationships built on trust.
10 Principles of Fair Trade
The WFTO prescribes the following as the 10 principles of fair trade:
1. Create employment opportunities in the developing world.
2. Practice transparency in communication and take accountability in actions.
3. Focus on improving the lives of producers through long-term agreements and interest-free cash advances.
4. Pay a fair wage to producer groups promptly and in the amount previously agreed upon by both parties.
5. Prohibit the use of child labor and forced labor.
6. Do not discriminate based on race, caste, ethnicity, religion, disability, gender, sexual orientation, political affiliation, HIV/AIDS status, or age.
7. Maintain safe and healthy working conditions.
8. Foster independence for producer groups by encouraging them to improve their internal management skills and access new markets.
9. Promote fair trade by raising awareness of the issues in the developing world and how ethical trade can improve the lives of producers.
10. Respect the environment by using responsible production methods.
Fair Trade Certifications

Fair trade coffee companies must meet the standards set up by fair trade organizations. They can then apply for fair trade certification and pay membership fees to fair trade associations. In order to maintain this certification, fair trade coffee brands complete an annual assessment that includes information such as how many times each producer has been visited to ensure that working conditions are up to par.
Peer reviews are also common in the certification process, meaning that competitors will assess each other and report back to their organization. That way, you can trust that a company that is fair trade certified is keeping up with all 10 principles of fair trade.
Once they are certified, they can put a Fair Trade Certified™ logo on their packaging.
Fair trade associations include:
- Fairtrade International
- FLOCERT
- Fair Trade Federation
- World Fair Trade Organization
How Does Fair Trade Relate to Coffee?
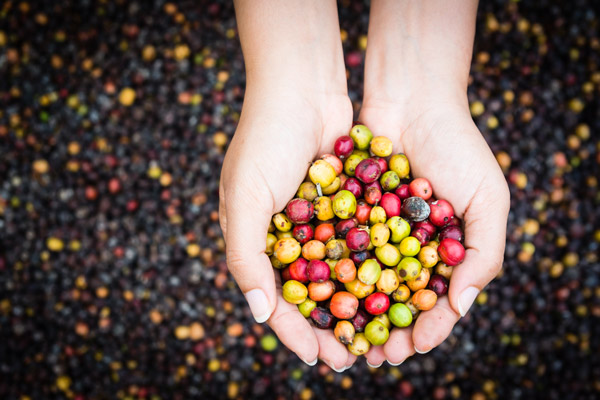

The best coffee in the world grows in a specific climate found in regions near the equator. Unfortunately, many of the countries where this climate exists face economic uncertainties due to governmental issues or other factors.
Second only to oil, coffee is the commodity with the highest volume being exported to the developed world. The high demand for coffee in North America and Europe creates an opportunity for farmers in developing countries to export their coffee. But it also means that is up to us as consumers to be aware of where our coffee comes from.
Fair Trade Coffee Pricing
Many times, farmers join together and form cooperatives in their communities. These cooperatives can sell their product to coffee companies based in North America and Europe. Fairtrade coffee companies work directly with farmers to agree on a price that will work for both parties, taking into account factors such as market value and operation expenses. Once a sustainable price is agreed on, the company will pay the farmers a portion of the order cost upfront. This helps the farmers cover their expenses until the order is complete, at which time they receive the remaining balance of their order price.
How Much Money Goes Back to Farmers?
A common misconception is that a portion of the price a customer pays for a fair trade item goes directly to the farmer. But really, the farmer will already have been paid in full by the time the product reaches shelves. The importance of buying fair trade commodities is that customers make it possible for fair trade organizations to continue placing orders from the developing world.
Often, coffee farmers will invest their earned profits in their communities for education, healthcare, the environment, or for improving living and working conditions. In order for these improvements to continue, it’s important that farmers receive consistent orders from distributors. But of course, distributors can only buy as much as they can sell. So it’s a cycle that’s largely controlled by consumers’ choice to buy fair trade.
Why Buy Fair Trade Coffee?
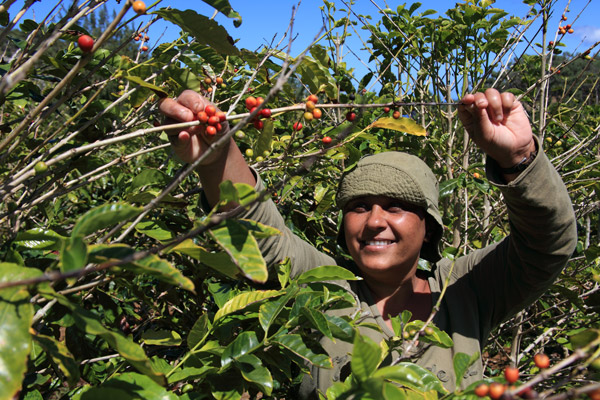

As people become more aware of problems in the developing world and the issues arising from unethical trading practices, more people are becoming conscious of where they spend their money. Consumers have the power to make a positive change through their purchasing decisions because if more people support fair trade coffee brands, companies will be pushed to embrace ethical business practices. By providing fair wages to farmers, prohibiting child labor, and mandating sustainable regulations, fair trade associations promote healthier, happier lifestyles for communities in the developing world.
While the focus of fair trade is to improve the lives of people, the coffee produced under fair trade conditions is often of better quality than standard trade alternatives. This is because corners are not cut at any step of the process. For example, protecting the environment not only protects farmers against harmful chemicals, but also yields a healthier coffee plant with more flavorful berries. So not only does fair trade coffee support farmers in the developing world, but it tastes great too.
When your company buys fair trade certified coffee brands, it is choosing to support equality for coffee farmers, sustainable business practices, and environmental responsibility. The purchase of fair trade coffee enables communities to become self-sufficient as they use their earnings to contribute to local education and healthcare.
How to Buy Fair Trade Coffee
When purchasing different kinds of coffee beans, you should look for a fair trade-certified logo. Many companies are not strictly fair trade, but they may offer some fair trade products. Some grocery stores and co-ops may have aisles dedicated to fair trade products. If you’re buying coffee in bulk online, product descriptions will mention Fair Trade and packages will show a Fair Trade Certified™ logo. You just need to look for them.
Some good fair trade coffee brands include:
- Equal Exchange
- Level Ground
- Serrv
- Pura Vida
- Higher Grounds
- Cafe Direct
- Grumpy Mule
What’s the Difference between Fair Trade and Direct Trade?
Another thing you may have heard about while shopping for coffee is “direct trade.” The similarities between fair trade and direct trade are that they both cut out the middleman, meaning that green coffee buyers work directly with coffee farmers. Another similarity is that the result of building a long-term buying relationship yields a better quality of coffee and a better quality of life for farmers.
Goals
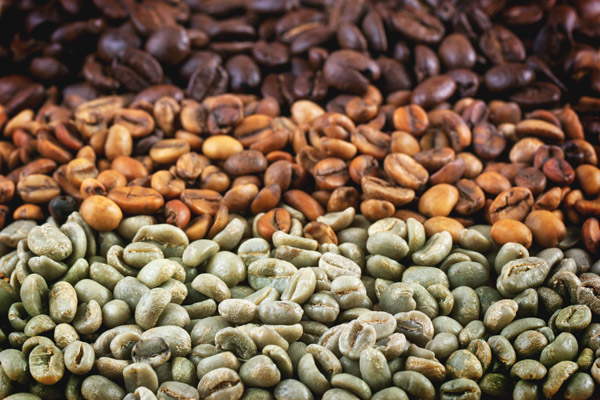

The main difference between fair trade and direct trade is that they have different end goals. Fairtrade was built to improve the lives of farmers, while direct trade places its focus on the quality of their coffee. But, just like fair trade’s social standards result in a better quality product, direct trade’s commitment to a high-quality product winds up helping farmers.
Better quality requires long-term trading relationships and environmental responsibility, neither of which can be achieved without transparency, accountability, and fair wages. So, even though each of these trade movements has a different focus, they are both good options to consider when stocking your cafe.
Certifications
Another difference is that while fair trade must be certified by a third-party fair trade association, direct trade does not have a legal definition and each company defines what direct trade means to them. Since there is no certification process in place for direct trade at this time, you won’t see a direct trade logo on packages. This can make it harder to distinguish true direct trade brands from brands that use the term simply for marketing purposes. So, before buying a direct trade brand, it may be a good idea to check out their website and read about their sourcing standards.
Fair Trade vs. Direct Trade
| Fair Trade | Direct Trade |
| Standards are regulated by third-party non-profit organizations | Standards are regulated by individual companies |
| Main objective is to improve the lives of farmers (but has a great quality as a result) | Main objective is to improve the quality of coffee (but improves lives as a result) |
| Fair trade-certified brands will have a logo on the packaging | There is no official direct trade certification or logo at this time |
It is always a good idea to research brands and companies online prior to buying their coffee. Not only does coffee sourcing affect working conditions for farmers and the strength of their communities, but it is also a factor in the quality and flavor of the product itself. So the more you know about a brand, the more confident you can be about providing your guests with a good product.





.jpg)